Amazon is one of the world’s leading and most influential companies. It was founded by Jeff Bezos in 1994 as a bookstore primarily, which then turned into an online marketplace. Its headquarters are now in Seattle, USA. Amazon has been publicly listed on NASDAQ since its IPO in 1997.
Amazon is a pioneer in the e-commerce retail business. It now offers many services beyond e-commerce, including cloud computing, online books, software, electronics, self-driving cars, etc. Amazon operates its logistics and supply chain network through its regional headquarters in many countries.
Overview
Amazon’s financial strength is well known, with a current share price of $ 3,186 and a total market cap of $ 1.63 trillion. It owns around 19 subsidiaries and operates globally through its regional headquarters.
Amazon hired more than 400,000 new employees globally in the past year alone. It now has a staggering more than 1.0 million employee workforce.

Amazon offers products and services to both retail and corporate customers. Its products and services can also be categorized on a digital and non-digital basis. Amazon offers E-Books, Streaming videos and music, E-commerce products, Software, and other IT products and services.
The Company Profile
| Company Name | Amazon.com Inc. © |
| Website | Amazon.com |
| Founded- In: | 1994 |
| Headquarters: | Seattle, Washington, US. |
| Founder, President, CEO, and Chairman | Jeff P. Bezos |
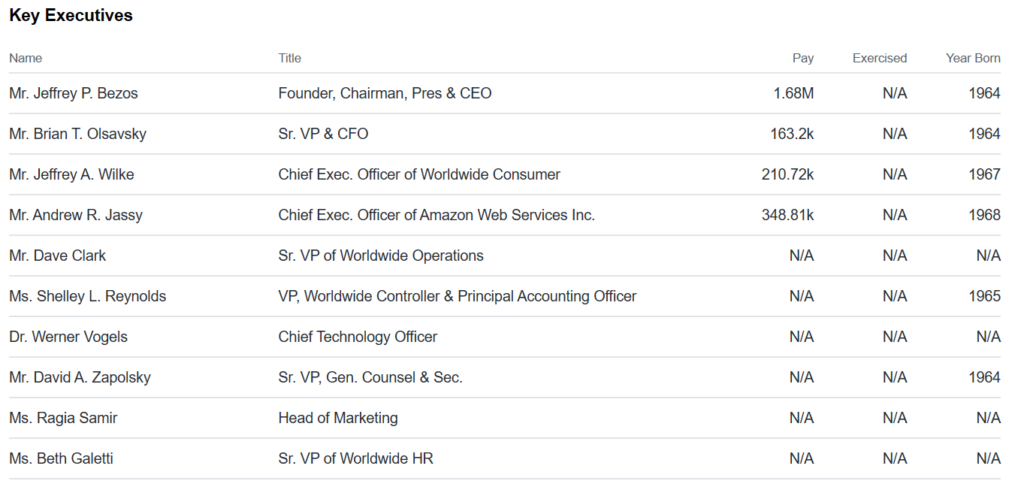
| Key People | Jeffery M. Blackburn Andrew R. Jassy Jeffery A. Wilke Sr. VP, Business Development CEO Amazon AWS CEO Worldwide Consumer |
| Business Model | E-commerce, Web Service, Entertainment. |
| Product/Services | E-commerce, Digital Content, and Devices, Software Cloud computing Industrial Products and Services. |
| Competitive Advantage | Technology, Brand Recognition, International Presence, Financial Strength. |
| Revenue | $ 347.946 Billion as of 30th September 2020. |
| Competitors in different fields of business | Target, Walmart, Costco. Oracle, Microsoft, IBM. Netflix, Apple, and Google. |
Here is a brief company profile for Amazon. Amazon owns around 20 subsidiaries and operates worldwide through its regional headquarters.
Amazon Business Model
Amazon offers a comprehensive online marketplace business model. It can be dubbed as a combination of e-commerce and reseller markets simultaneously.
Amazon generates revenue by selling consumer products directly through its different regional websites. It also allows sellers to partner with it and offers a commission-based business model.
Amazon describes its business model into different categories:
- E-commerce through its Online stores
- Amazon Physical Stores, through its subsidiary Whole Foods Market
- Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- Third-party seller revenue through e-commerce and affiliates
- Subscription-based revenue from its Amazon Prime customers
Amazon calls its inventory of products and services “earth’s biggest collection.” If you can go through all the types of products and services on offer, you’ll feel the claim isn’t imprecise.
- Amazon Digital Streams, Movies, TV Streams, Music, CDs, and Downloads
- App Store for Android, including games
- A range of Amazon Software collection
- Amazon Web Services
- Retail E-Commerce selection includes Arts and Crafts, Fashion, Electronics, toys and gaming, home appliances, Auto accessories, Computers, etc.
- Amazon Kindle E-readers and Books
Amazon SWOT Analysis – Strengths
Amazon is the world’s leading e-commerce platform. It has lived up to every challenge so far and reached an unmatched level of success, from its tech development to its leadership and expansion to its financial strengths.
Global Brand Recognition
Amazon enjoys the world brand recognition that only a few companies can gain.
Here are some key figures for the Amazon user base:
- Amazon had 150 million Prime paying users worldwide as of 2019
- Amazon’s US website alone brings 212 million + monthly visitors
- Amazon holds approximately 14% of the total global e-commerce trade
Since its inception in 1994, Amazon has evolved from a bookselling company to an e-commerce leader. Amazon is expanding its services beyond e-commerce, software development, and Mobile Apps.

Financial Strength
There are very few companies that stood up against the last year’s pandemic-caused recession. Amazon is one of the companies that outperformed the stock market even in crises.
Here are Amazon’s key financial figures:
- The current share price is a staggering $ 3186.73 as of now
- Total Market Capitalization of $ 1.63 trillion
- Amazon’s 2019 financial revenue stood at $ 280 B. Its current revenue is $ 347.946 B.
- Amazon has total assets of $ 282 billion and a shareholders’ equity of $82.775 billion.
- Its cash-on-hand current balance is $ 68.042 billion.
Global Presence and Operations
Amazon is a global e-commerce giant. It has expanded its global reach to almost every country in the world. It’s one of the biggest strengths in its global warehouse presence.
These global warehouses and regional headquarters allow Amazon to provide ultra-fast services to its customers worldwide. Amazon’s global supply chain network remains one of its core competitive edges.
Technology and Innovation
Amazon stayed ahead of the e-commerce competition through its unmatched technological development and innovation. By the time its competitors could match its global e-commerce reach.
Amazon has diversified into Web services, IT, App developments, and Energy investments. Today Amazon’s AWS contributes almost 21% of its total global consolidated revenue.
Some other essential Strengths:
- Comprehensive retail merchandise availability to its consumers.
- Unique e-commerce platform offering products to retailers and industrial consumers alike.
- Wide range of products, including consumer products, web and IT services, and Mobile Apps.
- Affiliate and Reseller program for partners.
- Specialization and innovation through subsidiary acquisitions.
- Large supply chain networks through regional warehouses worldwide
Amazon SWOT Analysis – Weaknesses
Amazon is undoubtedly one of the leading companies in the world, but it still incorporates some weaknesses in its business model.
1) Rising Concerns on Amazon Product Quality
Amazon allows third-party reselling with its partner and affiliate program. This has led to several consumer complaints about receiving low-quality, counterfeit, and even discarded products. Apple filed a lawsuit against Amazon and provided substantial evidence of selling its counterfeit products.
2) Internet-connected customer base only
Amazon is mainly an e-commerce retailer, which limits its access to global consumers. It competes with e-commerce retailers like Alibaba on one side and traditional retailers like Walmart and Costco.
The global e-commerce share still holds only a fraction of the total trade volume. Thus Amazon heavily relies on internet-connected consumers only.
3) Scattered focus with diversification
Perhaps Amazon’s biggest strength has been its innovative diversification by acquiring many subsidiaries over the years. It also possesses a potential weakness of Amazon, as it now focuses broadly on other than e-commerce products like AWS, Software development, and media streaming.
4) Seasonal Growth Vulnerability
If we carefully examine Amazon’s quarterly financial statements, they reveal a seasonal revenue hike in the last quarter. Even Amazon admits it is a financial risk in its published financial reports.
Any occurrence such as the current coronavirus can heavily damage its yearly revenues and thus impact its total market capitalization.
5) Low-Profit Margins
Amazon’s revenue and gross profit margins as a retailer are substantially high. Its net profit margin of 4.99% is higher than Walmart (3.60%) and Costco (2.40%). But its main e-commerce competitor, Alibaba, enjoys a net profit margin of 22%.
Also, its other competitors in sub-categories have significantly higher net margins, e.g., Microsoft 32%, Apple 20.9%, and Netflix 11.8%.
Amazon SWOT Analysis – Opportunities
Amazon acquired several subsidiaries to maintain a competitive edge over its competitors. Its CEO and founder Jeff Bezos still holds ambitious plans for Amazon’s expansions.
If we only predict the ongoing Amazon plans and its announced future expansions, they already provide a glimpse of opportunities for them.
- Amazon plans to introduce its fleet and logistics services.
- It plans to introduce innovative delivery services through drones and uncrewed vehicles.
- Ambitious plans for introducing an air fleet for amazon
- Entering into the Pharmacy business
- Amazon is investing in self-driving cars
- Cashier-free stores through Amazon Go
Amazon may soon introduce its physical store outlets, which contradicts its prime business model.
Amazon SWOT Analysis – Threats
There is hardly a potential threat for Amazon with its internal factors. Apart from its financial modeling for pricing and seasonal revenue reliance. However, Amazon does face potential external threats from its competitors and legislators.
Some of the key threats for Amazon are listed below:
- Amazon’s business model is easily replicable, making e-commerce entrants a significant threat.
- Amazon is prone to Cybersecurity threats, much like any other e-commerce retailer.
- Amazon’s one significant weakness is its reliance on North American region sales. It accounts for 61% of its total net sales as compared to only 27% of international sales.
- Amazon faces litigation and lawsuit petitions such as tax avoidance and counterfeit products.
- Amazon also faced litigation charges from the EU commission.
- It faces severe competition from a wide range of business sector companies.
- Amazon faces reputational risks with Human rights violation criticism, environmental impact, and employee working conditions.
Amazon has often been criticized for influencing its customers with fake reviews and products from third-party sellers. However, Amazon’s biggest threat remains its fast growth and ambitious diversification plans. Failing any significant growth or expansion plan can significantly harm its global brand recognition.
