I shouldn’t believe you if you say I have never used ZOOM in the last few months. Perhaps the most widely used service was ZOOM in the last few months of the Pandemic.
We were all forced to work from home and communicate remotely with our colleagues or students. The education sector, in particular, required dedicated remote video communication services as the educational institutes went on full shutdown.
Introduction
ZOOM Video Communication was founded in 2011 by Eris S. Yuan in the US. It started with a clear vision of providing video communication in an effective and modernized way. The company, thus far, has extended the services to more than 55 counties directly.
ZOOM’s best-selling product has been the meeting, chat, conference room, and events. Its sophisticated software and APIs for developers allow third-party integration. Video calling, live events, and webinar hosting are the most popular services offered by ZOOM.
The Business Model
ZOOM offers a free user account with reasonably limited features. Its main business revenue is generated from its paid subscription pricing plans on a monthly and annual basis.
ZOOM offers customized support and pricing plans for its large corporate customers. Both individual and corporate users are the customer base for ZOOM globally.
ZOOM’s main selling products in 2022 are:
- Meeting and Chat
- Rooms and Workspaces
- Video webinar and conference connector
- Zoom for developers
- Zoom for marketplaces
- On Zoom (BETA Version)
All of these services are equally useful for individual and corporate customers. However, Zoom has been improving the HD video conferencing experience to provide its corporate customers with customized services.
Company Profile
| Company Name | ZOOM Video Communication Inc. © |
| Website | zoom.us |
| Founded- In: | 2011 |
| Headquarters: | San Jose, California, US. |
| Founder | Eris S. Yuan (CEO) |
| Key People | Alchemy Sankarlingam (President of Product), and Brendon Ittelson Aparna Bawa (Engineering Chief Technology Officer COO) |
| Business Model | Software as Service (SAAS) |
| Product/Services | Video Calls, Meetings, Chat, Webinar, Phone (internet). |
| Competitive Advantage | Technology, Brand Recognition, International Presence |
| Revenue | $ 6.227 million as of 31st January 2020. |
| Competitors | Google, Microsoft, Cisco, Huawei, Adobe, 247Meeting, TeamViewer, and Adobe |
Here is a brief look at the ZOOM company profile and its key people.
Let us discuss some key strengths and weaknesses of ZOOM before we move on to the future opportunities and threats section to complete our SWOT analysis.
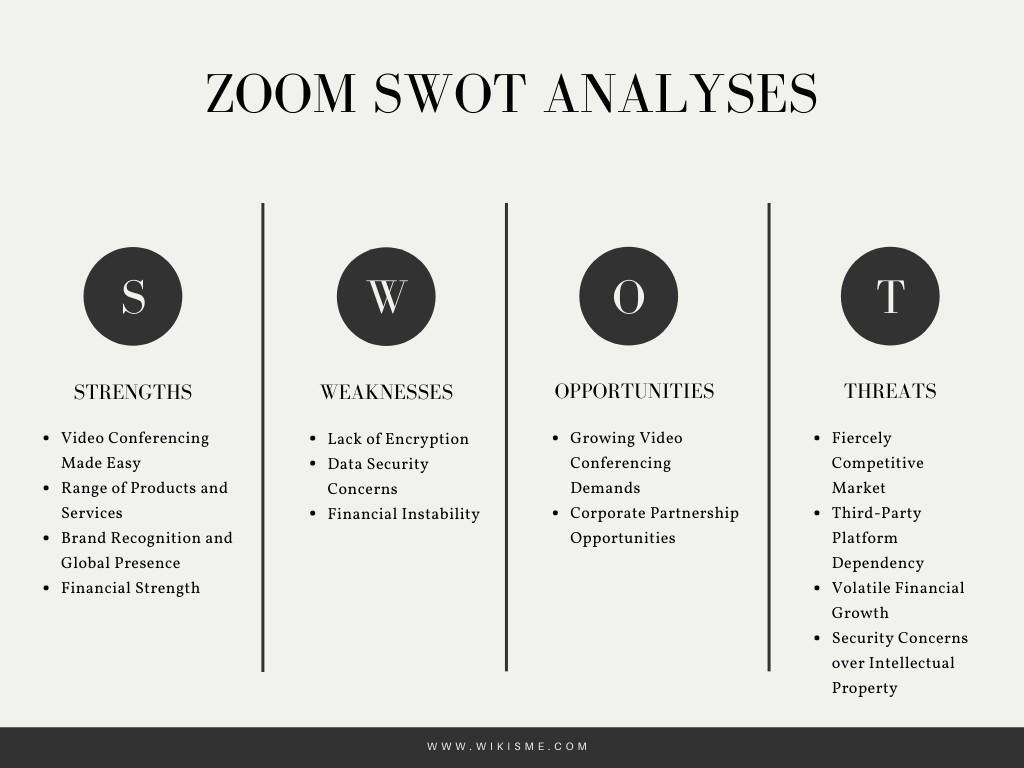
I) ZOOM’s Strengths
If the current Pandemic offered anything good, it was an opportunity for the technology companies like ZOOM and Facebook to grow even faster.
Zoom video conferencing solutions are web-based and available globally. Its services matched the much-needed remote communication requirements for individuals and corporate institutes in recent months.
Video conferencing and remote working has been on the rise well before the pandemic. In particular, more employees suggested likely adopting the remote working style. That scenario offers a significant growth opportunity and reception thus far from Zoom video services.
1) Video Conferencing Made Easy
Zoom did not pioneer video conferencing technology; it existed well before 2011. Zoom prioritized the ease-of-use experience for the customers. Its sophisticated technology and open-source API platform are well-received among users globally.
Zoom’s best strength is its technological products and services. Although it’s a relatively newer brand and still in the growth phase, it has established its mark amongst the industry leaders like Google, Microsoft, and Cisco.
2) Range of Products and Services
Zoom has the core product of video conferencing and webinar solutions. That attracts both individual and institutional clients globally.
Zoom’s neat User interface and third-party integration make it an affordable telecommunication tool. It mainly started with video conferencing and chatted features but now has extended the product range to Internet phones and webinars.
3) Brand Recognition and Global Presence
Zoom provides an all-in-one video, chat, screen sharing, and calling feature for free. It soon attracted a global audience. Its collaboration and resource-sharing platform for teams made it an attraction for institutional usage for education and business communities alike.
Zoom has a well-recognized brand reputation as its strength which is evident from its perceived global increased demand.
As of the last year (before the Covid- 19 increased demand), it had reached 300 million daily meeting participants over its network.
4) Financial Strength
Zoom remained a privately held company till 2019. It incurred accumulated losses till the 2018 financial year. After the share listing on NASDAQ in April 2019 and with current skyrocketing growth, the company has found financial stability too.
Its IPO valuation was $ 1 billion on the first day, which has to date reach well above $130 billion by September 2020.
II) ZOOM’s Weaknesses
Zoom’s open-source API and code access provide integration access and customization to the developers. Its easy-to-use interface has attracted a large global audience.
However, corporate and business users have been critical of the platform with security concerns.
1) Lack of Encryption
Zoom has been most widely criticized for its platform’s lack of encryption ability. Large corporate entities, governments, and sensitive business institutes have been reluctant to use the Zoom video conferencing platform.
Although the company announced end-to-end encryption in all its communication products, experts still lack trust in the claims.
2) Data Security Concerns
Apart from the obvious lack of Encryption features, Zoom faced another severe criticism: the security of user data. Critics claimed that some of the Zoom applications communicated through the “Chinese” servers even though both users were outside of China.
The lack of security for cloud data for its customers is another flaw in its widely perceived valuable communication technology.
3) Financial Instability
Zoom reported net annual profits after 7 years of operations. For a tech-based brand like Zoom with such a global audience, the pace of achieving financial stability does not match.
In the early years, it received an initial investment of $ 3 million from WebEx founder Subrah Iyar. Zoom has received additional investment from multiple funding rounds totaling over $146 million.
The company only reported net profits in the last two years of its operations after an IPO in April 2019. However, it is likely to report high profits in the current years, as the current pandemic crises drive highly volatile and seasonal financial growth.
III) ZOOM’s Opportunities
Zoom has finally made its mark in the global video conferencing industry. The pandemic crises opened new doors of opportunities for tech firms like Zoom.
1) Growing Video Conferencing Demands
Zoom reached the 300 million daily meetings limit, up from 10 million in December 2019. Although the significant trend surge is primarily driven by the current Covid 19 crisis, the usage is likely to grow in the coming years too.
Zoom has focused on institutional clients with ten or more users in the last few years. It has already announced plans to partner with startups and provide corporate users with customized solutions.
2) Corporate Partnership Opportunities
The work-from-home demand will likely increase, and the trend will likely rise in the coming years. More businesses require customized communication needs for employees and their customers.
Zoom has already responded with customizable SDK and better API offers for corporate customers.
Zoom has recently launched an event hosting product, “onZoom.” The education and health sector will likely see increased video conferencing demands in the next years.
If Zoom can keep up with the pace of the competition, it’s likely to see sustainable growth in the next few years.
IV) ZOOM’s Threats
Zoom operates in a highly fast-paced technology industry. Meeting customer expectations and matching the competition always poses risks of business failure.
Its competitors are industry leaders like Microsoft and Google, with unmatchable worldwide operations. It will always be challenging for Zoom to make a mark in such a highly advanced and saturated industry and sustain its growth.
1) Fiercely Competitive Market
Competing with global brands like Microsoft, Google, and Cisco would never be easy for any firm. Zoom faces severe competition with well-established and global brands in the video conferencing industry.
Zoom will have to provide a marketing edge for its customer base with either new products or higher value for money.
The company recently launched new products like its cloud-based Zoom Phone and OnZoom events. Yet the market competition remains the biggest business threat for Zoom.
2) Third-Party Platform Dependency
One of the core drawbacks that Zoom sustains is its product dependability on third-party platform services. Zoom users require priced hardware, internet, and networking infrastructure (corporate users) to utilize Zoom products fully.
The pricing plans offered by Zoom are not the final cost incurred by the end user. Higher total video communication costs may pose a significant business risk for the company in the coming years.
3) Volatile Financial Growth
As we witnessed, Zoon faced problems attracting after-seed investments in the early years of its inception. Its current market valuation after an IPO is skyrocketing. But the high growth stock valuation has taken a setback with the normalization of businesses globally.
It indicates a further slump in its future stock and perhaps the total growth over the next year. Zoom’s current financial gains cannot be interpreted as sustainable financial growth as the large-scale sales are largely pandemic-driven demand.
4) Security Concerns over Intellectual Property
Zoom also faces a business risk over the criticism of the lack of data security. In particular, government and large institutional users will remain skeptical of using Zoom services.
Although the company has introduced its new end-to-end encryption (E2EE) features, restoring customer trust will take time.